Generally, the assembled printed circuit board required a conformal coating finishing only when they are used in some mission-critical applications, such as aerospace, automotive, medical, military, etc. Nowadays, increasing demand in wearable electronics has lead to a higher requirement to the protection and reliability offered by conformal coating (the sweat will take problem between PCB and electricity).
Conformal coating is a specially protective polymeric film-forming material that protect printed circuit boards and electronic assemblies from harmful environmental impact such as moisture, corrosion, static, thermal shock, vibration, and even contamination. The coating formed as a thin film that “conform” to the contours of PCB and it’s components providing increased dielectric resistance, operational integrity, and reliability.
What is a Conformal Coating ?
Generally, conformal coatings are made of a polymeric material such as resin, sometimes mixtured with one or more solvents to enable the material to dispense and flow properly.
The best type of coating material to choose is subject to the exact protection requirement for electronic device and the specific environment that the electronic board will be located. Additionally, some important factors need be considered such as method of application, ease of repair and rework, etc.
Typical Conformal Coatings
Typically, conformal coatings are 1-part systems with a resin base, and maybe diluted with either chemical solvent or water in rare cases. As these coatings are semi-permeable, therefore they do not fully have water-proof or seal the coated electronic devices. The purpose of the coatings is to provide environmental and mechanical protection to significantly improve the durability, longevity and reliability of the electronic devices, and it is friendly to apply and repair.
Coatings can be categorized by their base resin:
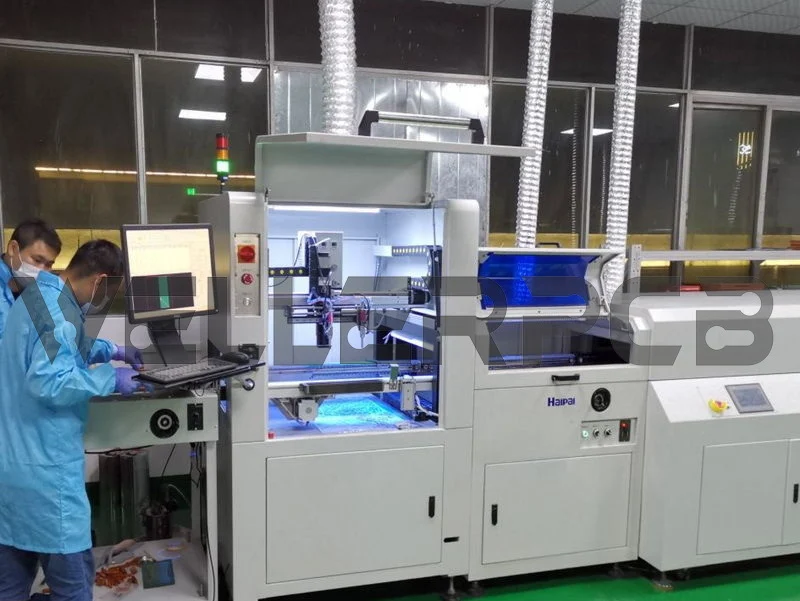

Automatic Conformal Coating Process
Why Use Conformal Coating?
Today, more and more complex electronics have to be exposed to harsh environments, so it is vital to have a necessary protection to ensure their normal function, durability, reliability, and longevity. Conformal coatings can provide proven protection against salt sprays, moisture, solvents and aggressive chemicals. What’s more, it is proved that a suitably chosen coating material can help reduce the effects of vibrations and mechanical stress on the electronic circuit board and its performance in serious temperature ranges. Conformal coatings are widely used in the electronic filed to protect the product, as well as enhance the reliability. Therefore, it diminish the destructive impact of early field failure and also reduces potential costs.
Is Conformal Coating Necessary?
Whether or not a coating needed to your electronic devices depending on the exact environment that the electronics will be used in, the sensitivity of the electronics, the durability and reliability required. Generally, the electronic devices manufactured and assembled by IPC class 3 are more likely to be coated due to their critical nature. Also, the increasing developing in miniaturization electronics and wearable electronics has raised up a higher demand for extra protection and reliability offered by conformal coating.
Is Conformal Coating Waterproof?
Typically conformal coatings can provide a moisture resistant layer of protection, but cannot be considered waterproof. As coatings are semi-permeable, so they can not fully seal the coated electronics or fully water-proof. They protect the electronics device from environmental exposure, improving the durability and reliability, and being friendly apply and repair.
How To Apply Conformal Coating?
Generally, the following factors should be considered when creating a conformal coating application process:
Common application methods for conformal coatings:

What A Thickness Should I Apply Conformal Coating?
The thicker the protective coating is not the better. Conversely, thinner coating provides the best production possible but minimizes other issues like heat entrapment, excess weight, etc. The typical conformal coating thickness is between 25-127um (1 to 5mils).
Generally, there are 4 ways to measure a conformal coating thickness:

How Long Does It have a Conformal Coating To Be Cured?
The exact time that the conformal coating can dry depends on the type of the resin, curing method, and the thickness of the coating, differently from seconds to days. Depending on the type of the resin chosen, several types of curing mechanisms are available:
Conformal Coating Removal
While there is a repair or rework on coated PCB, you may be required to remove a conformal coating from the printed circuit board to perform the related procedures. Generally, the methods and materials used to remove coatings are determined by the type of coating resins and the size of the coating area, and can impact the time required. The basic methods as specified by IPC are:
Solvent Removal– Although most conformal coatings can be dissolved in solvent, however it must be sure that the solvent used will not damage parts or components on the circuit board. Acrylic is extremely sensitive to solvent, hence it is the fastest and easiest coating to remove with solvent. Urethane and silicone coatings are the least sensitive to solvents, so it will need more soak-time and may require brushing to thoroughly remove the coating. And, parylene cannot be removed with solvent.
Peeling – Some conformal coatings can be peeled off from the printed circuit board. This is mainly a characteristic of some flexible conformal coatings and some silicone conformal coatings.
Thermal/Burn-through – A common technique of removing a coating is to simply burn through the coating with a soldering iron as the board is reworked or repaired. This method works well with most forms of conformal coatings.
Microblasting – Micro‐abrasive blasting is one of the most effective and safest methods to remove conformal coatings on delicate electronic devices. The removal is done by using a concentrated mix of soft abrasive and compressed air. This process is easy and very convenient while the removal on small areas of the conformal coating. It is most commonly used when removing epoxy and Parylene coatings.

Grinding/Scraping– This is a method to remove the coating by abrading the printed circuit board. This method is more effective and popular used in removing harder conformal coatings, such as epoxy, parylene and polyurethane. This method is only used as a option of last resort, as serious damages could be incurred.

Available Industry Certifications for Conformal Coatings
Certifications are used to specify conformal coatings from general-purpose varnishes and shellacs. There are several categories of user and industry specifications, but the two major certifications are most commonly referenced: but there are two major certifications most commonly referenced:
IPC-CC-830B / MIL-I-46058C
IPC-CC-830 revision B is a civilian version conformal coating qualification standard, the previous standard is MIL-I-46058C,which was inactive in November 1998. IPC-CC-830B is a battery of tests that includes appearance, UV fluorescence, insulation resistance, fungus resistance, flexibility, flammability, moisture and insulation resistance, thermal shock, and hydrolytic stability,and mostly used by board fabricators, OEM design engineers, and coatings suppliers.
UL746E
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) is officially considered a reliable and credible safety certification body worldwide, and UL certification is a common requirement for consumer goods throughout the world. UL746E testing for both the flammable safety and electrical safety of coated electronic devices. For electrical safety, there is a series of testing similar to IPC-CC-830B, but with a cycling current loading to constantly measure the failure of the isolative properties of the coatings, so as to evaluate whether a conformal coating can withstand sudden electrical surges and maintain its dielectric integrity. The flammability testing uses the UL 94 standard like IPC-CC-830B, which involves attempting to light the cured coating with an open flame, then observing the sustainability of the flame.
Once a conformal coating has passed UL746E, it can be registered with UL and get a registration number. Products certified and registered to UL746E standards can include the UL symbol (which looks like a backward “UR”). To maintain the registration, a coating must be retested annually.
The Most Common Conformal Coating Defects?
The following are the 7 most common causes of conformal coating defects we see, along with recommendations for how to avoid these:
WellerPCB® Conformal Coatings
WELLER offers a broad selection of high quality conformal coatings to our printed circuit board assemblies. Contact us now and we can help you find the best conformal coating for your electronics devices.