Sometimes the PCB quality issues is a headache once your expensive printed circuit board not worked as expected. It will bring disaster lost if your expensive boards failed in the mass assembly production even after rigorously verified and tested in prototype process. One of common reasons for circuit board failure is ionic contamination due to it’s exposure to moisture, dust, environment and residues left on the PCB board.
If ionic contamination not properly treated, it can take some potential risk such as PCB corrosion, electro-mechanical migration, parasitic leakage, dendrite formation. Therefore, in order to ensure durable reliability and avoid the short life cycle failures, it is necessary to have the PCBs tested for ionic contamination. Ionic contamination is done ROSE and ion chromatography tests. The ionic contamination analysis should be done following the specification detailed in IPC-TM-650 2.3.28.
More and more PCBs used in harsh environments, specially in some critical-safety applications such as nuclear energy, requires adequate electron-chemical reliability to control ionic contamination. The PCB production process includes at 20 chemical procedures, most of them involve extensive use of chemical ionic. Generally, contaminants can exist as ionic and non-ionic residues. Non-ionic residues are resin,oils, and grease. They don’t have conductive properties to remain on the printed circuit board surface after PCB assembly. Additionally,ionic contaminants can be organic/inorganic acids, salts, flux activators, and plating chemistries. Therefore, to maintain a high quality manufacturing process, it is very important to identify and control them.
What is Ionic Contamination in a Printed Circuit Board
Ionic contamination issues usually arise due to the ionic residues from bare printed circuit board production or from the chemical materials used in PCB assembly process. These residues can exist as various of substances including plastic, metal, and fiberglass granules, salts, oils, moisture, and dust. These ionic residues have a zero net charge (the composition of negative anions and positive cations) and get charged when a bare printed circuit board passes through multiple production processes. While in PCB assembly process, the electronic components also possibly carry various ionic/conductive contaminants along with fluids, biocides, and corrosion preventatives, etc. The treatment of the circuit board in the production process is also a major cause of ionic contamination in a bare printed circuit board.
Sources of Ionic Contamination in a PCB
Ionic contamination may come out during PCB manufacturing and circuit board assembly process. During PCB manufacturing, the PTH plating, circuit track etching process, and drilling are the potential sources of the contamination. While in PCB assembly process, flux residue in soldering, component biocides by pick and place machine, and ionic surfactants from solder preparation are potential source for PCB ionic contamination. Other most common sources of ionic residue including:
| Chemical plating: | Chemical etching and plating in PCB etching process are highly conductive and corrosive. It must be neutralized or rinsed them as they are a potential cause of leakage current. |
| Flux activators: | Commonly, the conductive flux residues from the soldering process include various binders, unreacted activators, saponifiers, and rheology elements. To avoid the potential risk of PCBA lifetime, these residues must be thoroughly removed by using solvent cleaning, say vapor degreasing, or by aqueous chemistries in the common batch. |
| Perspiration: | Before assembling the components on the bard printed circuit boards, you need to ensure no contaminants left from operation process. |
| Ionic surfactants and detergents | These must be removed to ensure non contaminants left on the circuit boards |
| Ethanolamines | A family of chemicals that work as surfactants and emulsifying ingredients in cleaning PCB assemblies. |
Impacts of Ionic Contamination in a PCB
In all PCB failure cases, approximately 15% of these occur due to contamination issues. In the PCB manufacturing process, the bare PCB can carry ionic contaminants in the form of left-over flux, etching chemical, and solder material. Once these residues remaining on the board, some major issues such as Electrochemical Migration (ECM), corroded traces, parasitic leakages, and dendritic growth, can directly have impacts on the printed circuit boards life-cycle.
Electrochemical Migration (ECM):
Electrochemical migration commonly occurs in the electric field in which metal gets dissolved, resulting in ion formation between two copper conductors. Once the electric field is applied, the metal dissolves at the Anode and gets deposited to the Cathode resulting in the growth of dendritic structures between anode and cathode. Because dendrites grow from conductive ions, they can mis-direct PCB currents from what should be, leading to short circuits. Dendrites create alternative current paths that can affect the accuracy of current measurements in a printed circuit board.
Corrosion:
Commonly, bare printed circuit boards corrode due to it’s material. Ionic contamination can expedite the corrosion of a PCB. When the ionic residue get in contacts with moisture, the short-circuit risk increases. The corroding metal falling off, need to know more about the chemical properties to have the operation correctly.
Ionic contamination along should not take the responsibility of the above consequences, other factors such as moisture and environmental exposure can also lead to corrosion. That is why printed circuit board must be baked to eliminate potential moisture before staring assembly process. The ionic contamination level need to be purposely controlled by adopting a process control tool during the manufacturing of bare circuit boards. This tool can ensure that the individual production process procedures are well performed in a purposely controlled manner to achieve a manageable ionic contamination level.
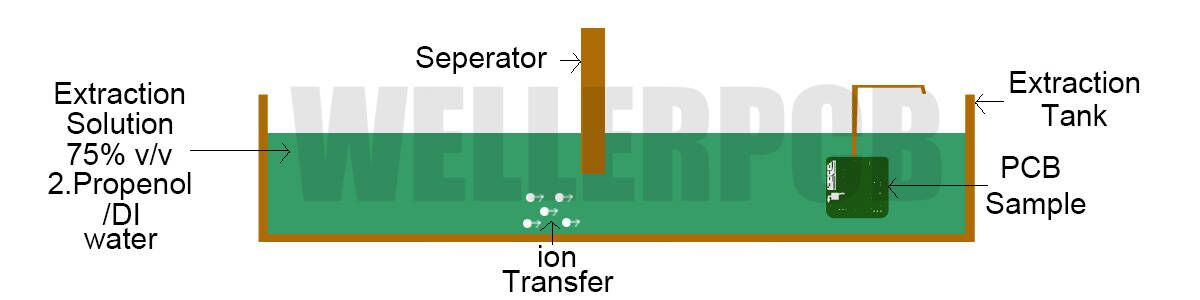
Ionic Contamination Testing in a PCB
Bad quality control and poor production process during PCB manufacturing, components assembly, and a sub-standard final cleaning are some of the major issues that lead to ionic contamination. It is critical to identify, control and avoid this issues. It can be done through proper ionic contamination testing and analysis via specific equipment. Typically, some well-known methods such as ROSE testing, ion extraction,and ion chromatography can do this well. Usually, it is necessary and worth to do humility validation testing at the beginning of the production.
To ensure the reliability and life-span of the printed circuit board, you’d better to ask your PCB manufacturer to provide the test report of ionic contamination before your formal circuit board assembly. This test will reduce the risk of defects cause by contaminants. Performing Ionic contamination test can also be used to detect the ionic residues resulting from the fabrication and soldering process. WELLER is available at any time for your ionic contamination test request for PCB fabrication and circuit board assembly.